
https://docs.nestjs.com/exception-filters
Documentation | NestJS - A progressive Node.js framework
Nest is a framework for building efficient, scalable Node.js server-side applications. It uses progressive JavaScript, is built with TypeScript and combines elements of OOP (Object Oriented Progamming), FP (Functional Programming), and FRP (Functional Reac
docs.nestjs.com
Exception filters
Nest는 애플리케이션에서 처리되지 않는 모든 예외 처리를 다루는 예외처리 레이어(exceptions layer)를 제공한다. 우리가 코드로 직접 예외 처리를 하지 않을 때 이 레이어가 자동으로 예외를 캐치해서 응답한다.
Throwing standard exceptions
우선 express에서 우리는 예외 처리를 할 때 일반적으로 다음과 같은 코드를 사용했었다.
...
throw new Error("No user");
...
반면에 Nest에서는 HttpException 이라는 클래스를 이용하여 에러를 처리할 수 있다.
@Get()
getAllCat() {
throw new HttpException('api is broken!', 401);
}
api를 날려보면 이에 해당하는 로그가 찍히는 것을 볼 수 있다.
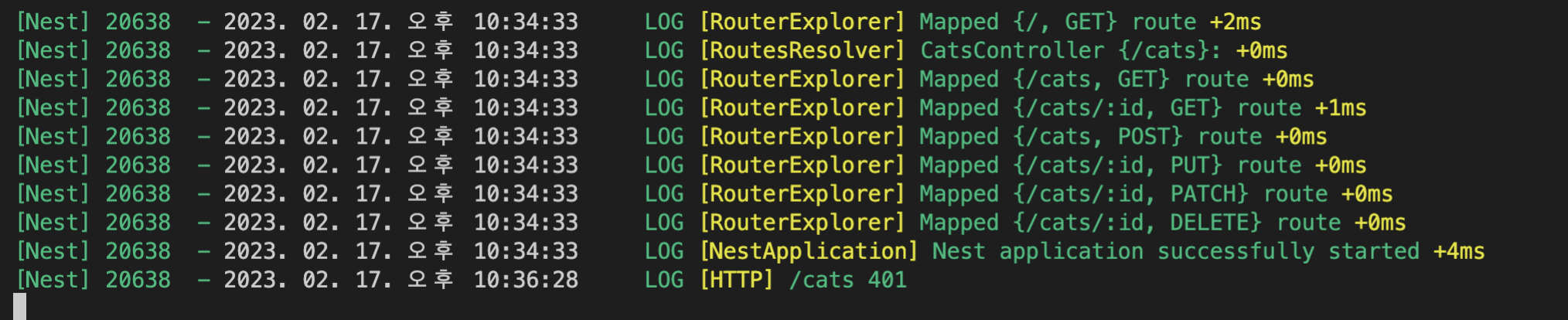
리턴값은 다음과 같다.
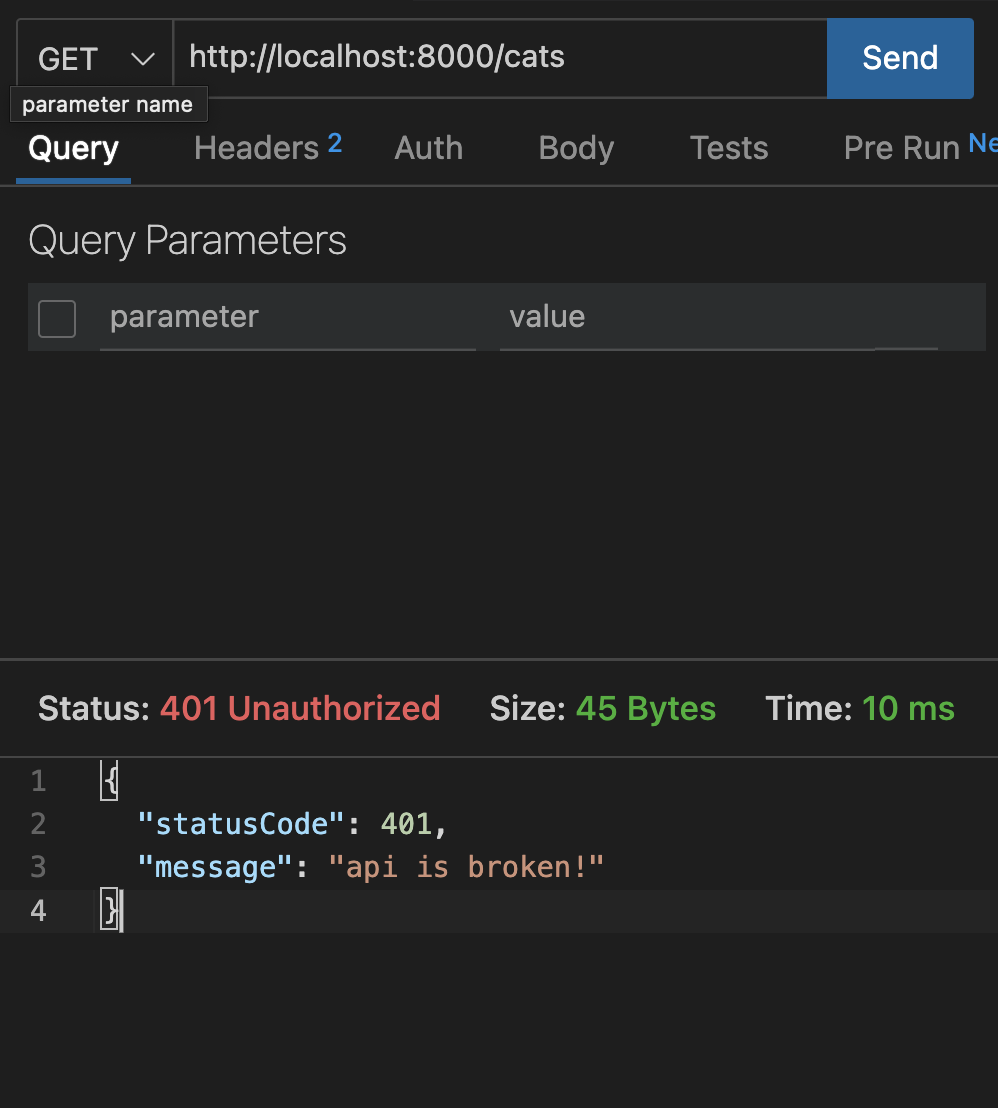
Nest에서는 기본적으로 다음과 같이 상태코드와 에러 메시지로 구성된 JSON으로 예외처리된 값을 보낸다. 하지만 현업에서는 프론트엔드 개발자들과 커뮤니케이션하면서 실제 서비스에 맞는 형식으로 오버라이딩하여 JSON을 반환해야 할 것이다.
예컨대 이런 식으로 커스터마이징할 수도 있다.
@Get()
getAllCat() {
throw new HttpException(
{ success: false, message: 'api is broken', haha: 'hoho' },
401,
);
...
}
반환되는 값은 다음과 같다.
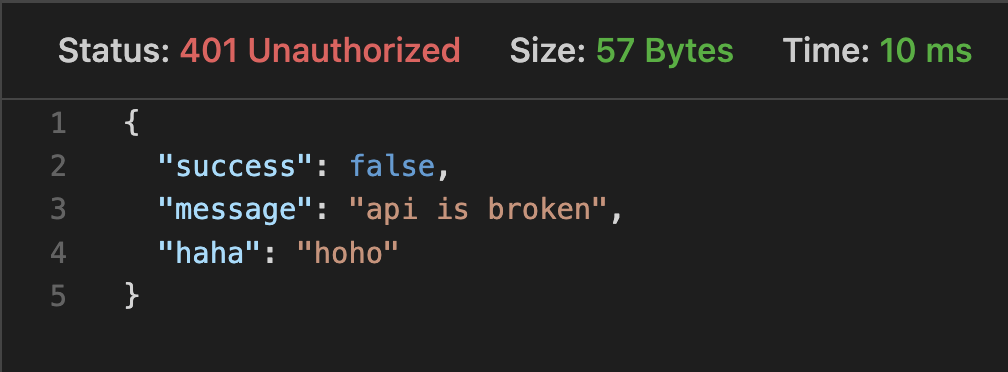
Custom exceptions
자주 필요하지는 않겠지만 예외를 커스터마이징할 수도 있다. 방법으로는 HttpException 클래스를 확장하여 서브클래스를 만들고, 예외를 상속받으면 된다.
export class ForbiddenException extends HttpException {
constructor() {
super('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}
}
Built-in HTTP exception
Nest는 기본이 되는 HttpException 클래스에서 상속되는 표준 예외들을 제공한다. 이는 @nestjs/common 패키지에 있다.
- BadRequestException
- UnauthorizedException
- NotFoundException
- ForbiddenException
- NotAcceptableException
- RequestTimeoutException
- ConflictException
- GoneException
- HttpVersionNotSupportedException
- PayloadTooLargeException
- UnsupportedMediaTypeException
- UnprocessableEntityException
- InternalServerErrorException
- NotImplementedException
- ImATeapotException
- MethodNotAllowedException
- BadGatewayException
- ServiceUnavailableException
- GatewayTimeoutException
- PreconditionFailedException
Exception filters
위에서 사용했던 Nest의 일반적인 예외 처리 방법에 대한 코드를 다시 보자.
@Get()
getAllCat() {
throw new HttpException(
{ success: false, message: 'api is broken', haha: 'hoho' },
401,
);
...
}현재 이 예외는 GET:: ../cats 일때 던져준다. 그런데 이 외에 다른 메서드와 엔드포인트들에서도 같은 형식의 예외를 사용한다고 하면 중복된 코드가 생길 것이고 이는 매우 비효율적이다. 현재 리팩터링 2판을 읽고 있어서 그런지 중복 코드에 대해서 더 민감하게 반응하게 된다..!
여하튼 코드의 중복을 방지하기 위해서 exception filters를 사용하면 된다. 우선 /src 레벨에서 http-exception.filter.ts 파일을 생성하고, 다음과 같은 코드를 작성했다.
import {
ExceptionFilter,
Catch,
ArgumentsHost,
HttpException,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
@Catch(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getStatus();
const error = exception.getResponse();
response.status(status).json({
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
error,
});
}
}먼저 catch() 메서드를 보면 exception과 host가 있다. exception은 여태 사용했던 그 예외 처리 객체다. host는 ArgumentHost 객체이다. 이 헬퍼 함수를 사용해서 예외가 발생한 컨트롤러의 요청과 응답 객체를 얻을 수 있다(자세한 건 여기를 참조하라고 한다. 다음에 더 깊게 봐보자!!). 그 이후 ctx라는 변수 안에 http context 인스턴스를 넣어서 HTTP 메서드들을 사용할 수 있게 한다. 그 이후 Express와 비슷하게 response에서 status와 json을 통해 예외 처리를 할 수 있다.
이 필터는 @useFilters 데코레이터를 이용하여 사용할 수 있다. 해당 데코레이터의 위치에 따라 특정 컨트롤러, 혹은 특정 메서드에서만 사용할 수도 있다. 만약 모든 cats 컨트롤러에서 동일하게 작동한다면 컨트롤러 데코레이터 아래에 넣으면 된다. 참고로 데코레이터는 아래에서 위의 방향으로 실행된다.
import {
Controller,
Delete,
Get,
HttpException,
Patch,
Post,
Put,
UseFilters,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { HttpExceptionFilter } from 'src/http-exception.filter';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
@Controller('cats')
@UseFilters(HttpExceptionFilter) // 여기!!!!
export class CatsController {
constructor(private readonly catsService: CatsService) {}
@Get()
getAllCat() {
...
throw new HttpException('No Authorization!', 401);
...
}
...
}
다시 요청을 보내면 다음과 같이 나온다.
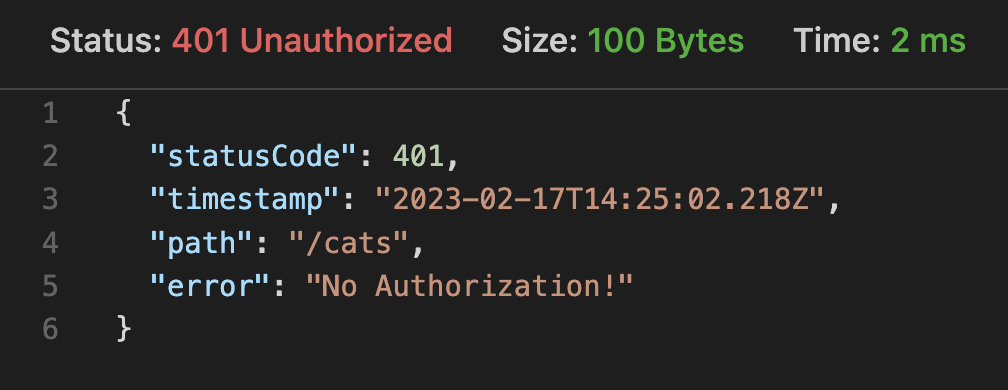
글로벌하게 사용하기 위해서는main.ts파일에서 @useGlobalFilters데코레이터를 사용하면 된다. 코드는 다음과 같다.
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { HttpExceptionFilter } from './http-exception.filter';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter()); // <--- 여기!!!!!!
await app.listen(8000);
}
bootstrap();
그런데 현재는 GET /cats 에 대한 예외처리만 한 상태이기 때문에 예외처리하지 않은 URL을 입력하게 되면 다음과 같은 에러 메시지를 보게 된다.
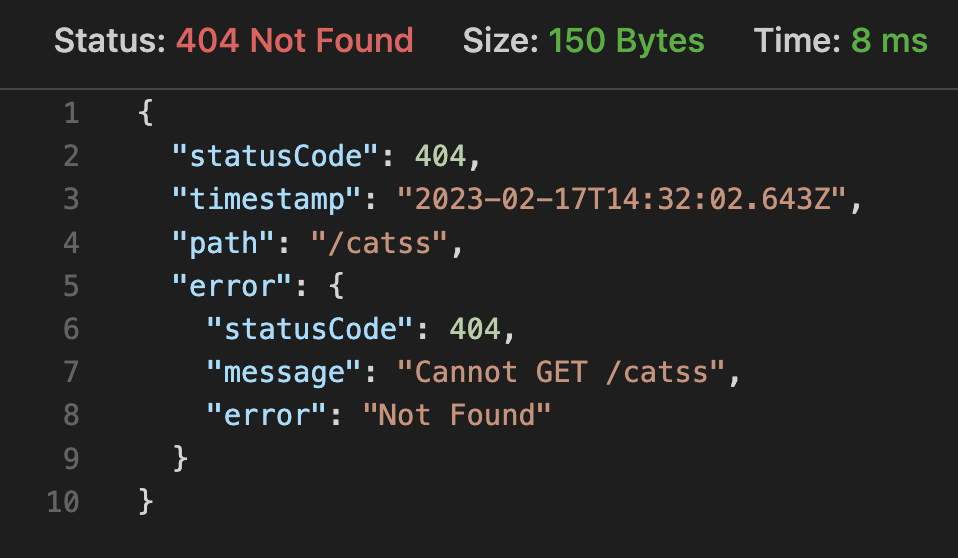
error 키값 안에 또 하나의 에러 객체가 들어가서 아주 못생긴 결과를 얻게 된다. error의 타입에 따라 다른 결과를 반환하도록 수정해보자.
import {
ExceptionFilter,
Catch,
ArgumentsHost,
HttpException,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
@Catch(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getStatus();
const error = exception.getResponse() as
| string
| { error: string; statusCode: number; message: string | string[] };
if (typeof error === 'string') {
response.status(status).json({
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
error,
});
} else {
response.status(status).json({
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
...error,
});
}
}
}error의 타입이 문자열이 아니라면 우리가 컨트롤하지 않은 부분에서 예외가 발생했다는 것이고, 그래서 리스폰스의 에러를 전개연산으로 펼쳐서 반환하도록 했다.
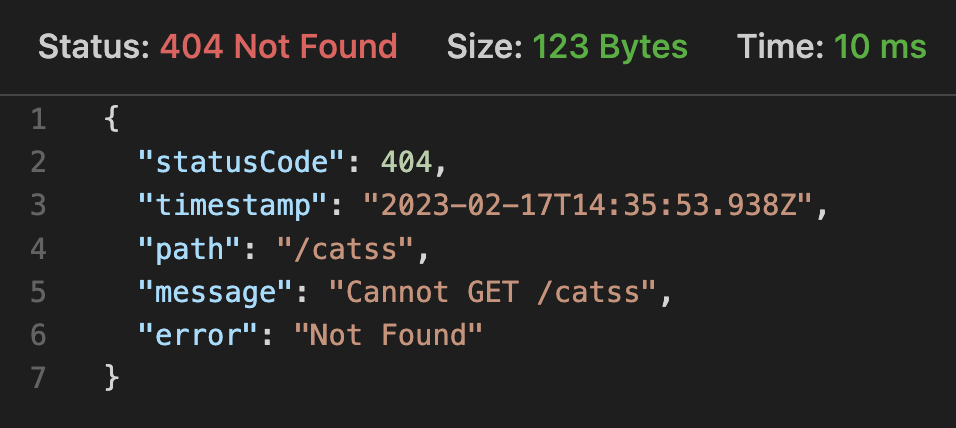
음 깔끔하다.
미들웨어 -> 컨트롤러 -> 서비스 -> 필터 -> 응답 이런 순서로 사용자 응답에 도달한다고 보면 된다.
'개발자 도전기 > [STUDY] JS || TS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| NestJS | docs | Guards (0) | 2023.02.24 |
|---|---|
| NestJS | docs | Pipes (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| NestJS | docs | Middleware (0) | 2023.02.16 |
| NestJS | docs | Modules (0) | 2023.02.16 |
| NestJS | docs | Provider (0) | 2023.02.13 |




댓글